Tropical Storm Idalia intensified early Monday and was expected to become a major hurricane before it reaches Florida’s Gulf coast, the National Hurricane Center said Monday, warning of an increasing risk of life-threatening storm surge and dangerous hurricane-force winds in Florida as soon as late Tuesday.
Heavy rainfall in western Cuba could produce flooding and landslides, forecasters said, and hurricane-force winds were expected later Monday.
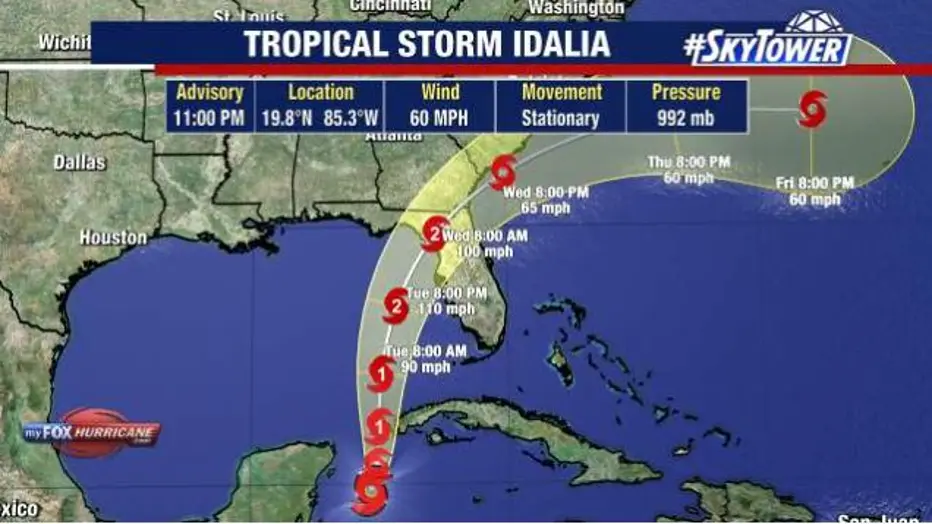
At 8 a.m. EDT Monday, the storm was about 90 miles (150 kilometers) off the western tip of Cuba with maximum sustained winds of 65 mph (100 kph). The storm was moving north at 8 mph (13 kph) at the time, the hurricane center said.
The center’s update also included a hurricane advisory for the Cuban province of Pinar Del Rio.
Forecasters said they expected Idalia to become a hurricane later Monday and a dangerous major hurricane by early Wednesday over the northeastern Gulf of Mexico.
Idalia was expected to move northward Monday, then turn north-northeast on Tuesday and Wednesday and move at a faster pace. The center was forecast to pass over the extreme southeastern Gulf of Mexico by early Tuesday, and reach the Florida’s western coast on Wednesday.
Along a vast stretch of Florida’s west coast, up to 11 feet (3.4 meters) of ocean water could surge on shore, raising fears of destructive flooding.
At a Sunday afternoon briefing, Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis noted that much uncertainty remains in the forecast.
“This thing hasn’t even gotten to Cuba yet, and the water in the Gulf is very, very warm and so that will provide some fuel for this thing to pick up some more speed,” DeSantis said.
Large parts of the western coast of Florida are at risk of seawater surging onto land and flooding communities when a tropical storm or hurricane approaches. That part of Florida is very vulnerable to storm surges, Jamie Rhome, deputy director of the National Hurricane Center, said Sunday.
“So it will not take a strong system or a direct hit to produce significant storm surge,” he said.
In Cedar Key, a fishing village that juts out into the Gulf of Mexico, a storm surge is among the greatest concerns, said Capt. A.J. Brown, a fishing guide who operates A.J. Brown Charters. The concern is that if the storm strikes Florida just to the north, Cedar Key would get the powerful surge that comes from being on the southeastern side of the storm.
There are worries in Cedar Key about a storm surge, Brown said. If it reaches five feet (1.5 meters) “it would cover most everything downtown.”
Mexico’s National Meteorological Service on Sunday warned of intense to torrential rains showering the Yucatan Peninsula, with winds as fast as 55 mph (89 kph).
It said the storm could cause anything from powerful waves to flooding in southern Mexico, mainly around coastal cities in the Yucatán and Quintana Roo states. It asked citizens to stay alert.
Florida has mobilized 1,100 National Guard members, and “they have at their disposal 2,400 high-water vehicles, as well as 12 aircraft that can be used for rescue and recovery efforts,” said DeSantis, the Republican governor who is a candidate for the GOP presidential nomination.
“If you are in the path of this storm, you should expect power outages,” he added.
So far this year, the U.S. East Coast has been spared from cyclones. But in the West, Tropical Storm Hilary caused widespread flooding, mudslides and road closures earlier this month in Mexico, California, Nevada and points to the north.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration recently said the 2023 hurricane season would be far busier than initially forecast, partly because of extremely warm ocean temperatures. The season runs through Nov. 30, with August and September typically the peak.
(AP)