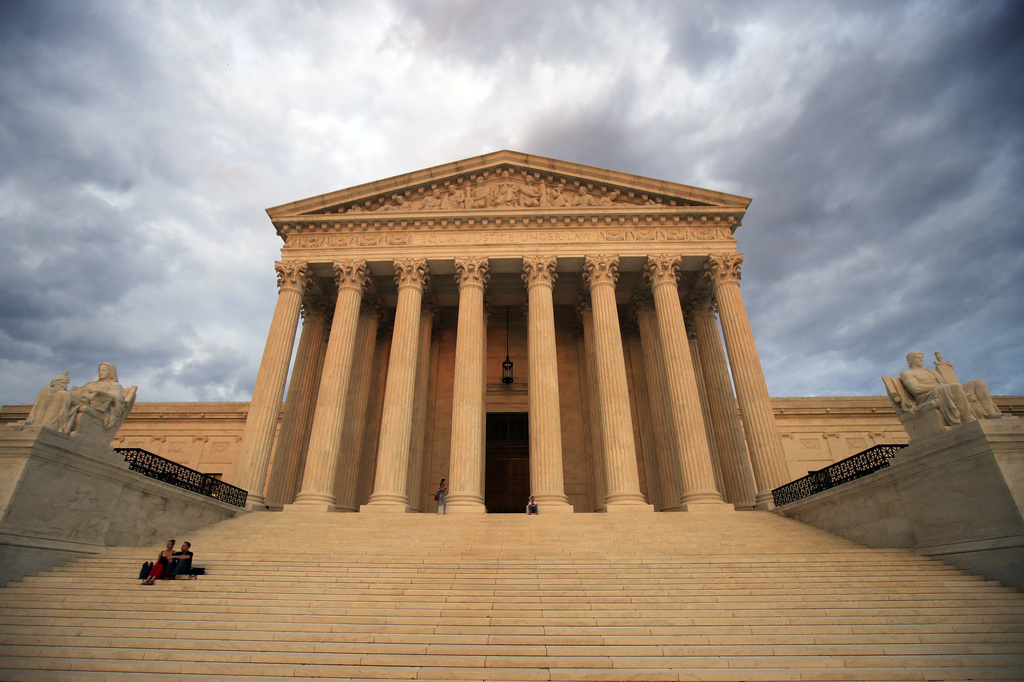
The Supreme Court is hearing arguments in a challenge to the Securities and Exchange Commission’s ability to fight fraud, part of a broad attack on regulatory agencies led by conservative and business interests.
The case before the justices Wednesday involves the Biden administration’s appeal of a lower-court ruling that threw out stiff financial penalties imposed on hedge fund manager George R. Jarkesy by the SEC.
The high court’s decision could have far-reaching effects on the SEC and other regulatory agencies, and it’s just one of several cases this term that could constrict federal regulators. The court’s conservative majority has already reined them in, including in last May’s decision sharply limiting their ability to police water pollution in wetlands.
Last year, a divided panel of the New Orleans-based 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled in favor of Jarkesy and his Patriot28 investment adviser group on three separate issues.
It found that the SEC’s case against him, resulting in a $300,000 civil fine and the repayment of $680,000 in allegedly ill-gotten gains, should have been heard in a federal court instead of before one of the SEC’s administrative law judges.
The panel also said Congress unconstitutionally granted the SEC “unfettered authority” to decide whether the case should be tried in a court of law or handled within the executive branch agency. And it said laws shielding the commission’s administrative law judges from being fired by the president are unconstitutional.
Judge Jennifer Walker Elrod wrote the appellate opinion, joined by Judge Andrew Oldham. Elrod was appointed by former President George W. Bush, and Oldham by former President Donald Trump.
Judge Eugene Davis, a nominee of former President Ronald Reagan, dissented.
Jarkesy’s lawyers noted that the SEC wins almost all the cases it brings in front of the administrative law judges but only about 60% of cases tried in federal court.
The SEC was awarded more than $4 billion in civil penalties in the 2022 government spending year, the Justice Department wrote in court papers.
A decision upholding the 5th Circuit’s ruling could sweep far more broadly, calling into question the authority of administrative law judges at numerous federal agencies, the Justice Department said.
A decision in SEC v. Jarkesy, 22-859, is expected by early summer.
(AP)











2 Responses
When the Supreme Court is discussing statutory interpretation (rather than the Constitution itself), all it takes is a simple statute (rather than a constitutional amendment) to change the law, thereby overruling the court decision. The issue is whether the Congress (which set up the agency) can authorize an agency to conduct judicial proceedings without the safeguards the Constitution provides – those cases could be tried by real judges with all the rights guaranteed by the Constitution (which might require having more judges which requires a simple act of Congress). It is very clear from history that when there is a national consensus, Congress is able to act quickly to resolve problem – and if there is no such consensus it is probably better that they do nothing.
This case would not only affect the SEC but also other regulatory agencies such as FERC which have similar inhouse adjudication procedures.